Introduction
A Java class defined within another class is called a nested class. Nested classes are of two types: static and non-static. Non-static nested classes are generally known as inner classes.
An inner class has direct access to all the fields and methods of its encompassing object, even if they are private:
class Outer {
class Inner {
long foo() {
//can access Outer's x
return x * x;
}
}
private int x;
}
Shadowing
A type (e.g., local variable, parameter, or field) declared inside a specific scope (e.g., a method, an inner class) can shadow a type declared in the outer scope if they have the same names. A typical example of shadowing is a local variable or a parameter of a method having the same name as of a class field. In that case, the class field can be accessed by qualifying it with this:
class A {
int add(int x) {
//parameter 'x' shadows field 'x'
return this.x + x;
}
protected int x;
}
Similarly, if a type declared in an inner class shadows its outer class's field (or method), the outer class's field (or method) could be accessed by a qualified name, as shown below:
class Outer {
class Inner {
long foo(int x) {
//parameter 'x' shadows Outer's x
//can access Outer's x as:
return Outer.this.x * x;
}
}
private int x;
}
Another Example and The Question
In the following code and design, a class Car comprises an inner class EngineEx instance, among other components. The EngineEx extends the Engine class to override and add some behavior specific to the Car, as shown below:
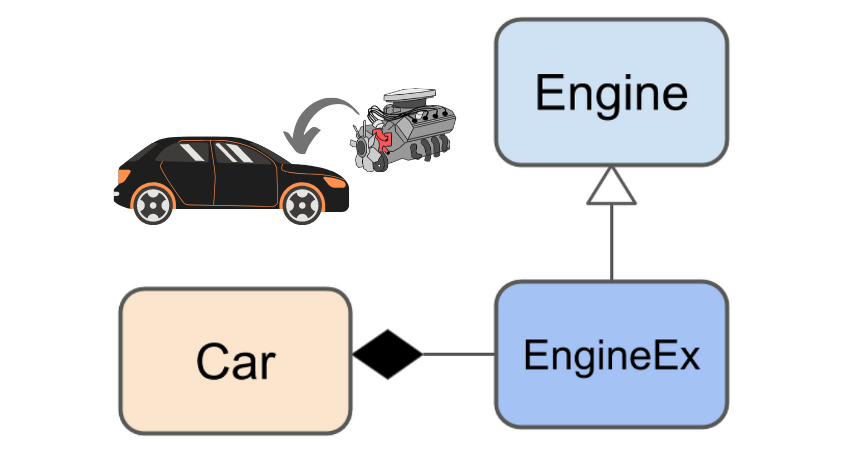
class Engine {
//more methods and fields...
String getName() {
return name;
}
protected String name;
}
class Car {
//more methods...
Engine getEngine() {
return engine;
}
private class EngineEx extends Engine {
@Override
String getName() {
return ____;
}
}
//more fields...
private EngineEx engine = new EngineEx();
private String name;
}
The EngineEx overrides a getName() method whose implementation is partially hidden (____). This method returns the Engine's name prefixed with the Car's name. Say, if Engine's name is "V8," and the Car's name is "Accord," the EngineEx's getName method returns "Accord V8":
var c = new Car();
/* If Car's name is "Accord" and Engine's name is "V8",
the following will print "Accord V8" */
System.out.println(c.getEngine().getName());
Select all the choices below that are the correct implementation (replace the ____ above) of EngineEx's getName method (Check Explanations for details):